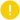
题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
(a) IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors contains guidanc
(a) IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors contains guidance on the use of accounting policies and accounting estimates.
Required:
Explain the basis on which the management of an entity must select its accounting policies and distinguish, with an example, between changes in accounting policies and changes in accounting estimates. (5 marks)
(b) The directors of Tunshill are disappointed by the draft profi t for the year ended 30 September 2010. The company’s assistant accountant has suggested two areas where she believes the reported profi t may be improved:
(i) A major item of plant that cost $20 million to purchase and install on 1 October 2007 is being depreciated on a straight-line basis over a fi ve-year period (assuming no residual value). The plant is wearing well and at the beginning of the current year (1 October 2009) the production manager believed that the plant was likely to last eight years in total (i.e. from the date of its purchase). The assistant accountant has calculated that, based on an eight-year life (and no residual value) the accumulated depreciation of the plant at 30 September 2010 would be $7·5 million ($20 million/8 years x 3). In the fi nancial statements for the year ended 30 September 2009, the accumulated depreciation was $8 million ($20 million/5 years x 2). Therefore, by adopting an eight-year life, Tunshill can avoid a depreciation charge in the current year and instead credit $0·5 million ($8 million – $7·5 million) to the income statement in the current year to improve the reported profi t. (5 marks)
(ii) Most of Tunshill’s competitors value their inventory using the average cost (AVCO) basis, whereas Tunshill uses the fi rst in fi rst out (FIFO) basis. The value of Tunshill’s inventory at 30 September 2010 (on the FIFO basis) is $20 million, however on the AVCO basis it would be valued at $18 million. By adopting the same method (AVCO) as its competitors, the assistant accountant says the company would improve its profi t for the year ended 30 September 2010 by $2 million. Tunshill’s inventory at 30 September 2009 was reported as $15 million, however on the AVCO basis it would have been reported as $13·4 million. (5 marks)
Required:
Comment on the acceptability of the assistant accountant’s suggestions and quantify how they would affect the fi nancial statements if they were implemented under IFRS. Ignore taxation.
Note: the mark allocation is shown against each of the two items above.
 答案
答案